中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (37): 6636-6640.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.37.015
• 组织构建与生物活性因子 tissue construction and bioactive factors • 上一篇 下一篇
眼针治疗急性脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠海马组织细胞间黏附因子1的变化
潘 茜,王 哲,高 原,于 丹,王 莹,井 欢,王守岩,王 健,关洪全
- 辽宁中医药大学,辽宁省沈阳市 110847
Eye acupuncture therapy affects intercellular adhesion molecule 1 expression in rat hippocampus of acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
Pan Qian, Wang Zhe, Gao Yuan, Yu Dan, Wang Ying, Jing Huan, Wang Shou-yan, Wang Jian, Guan Hong-quan
- Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
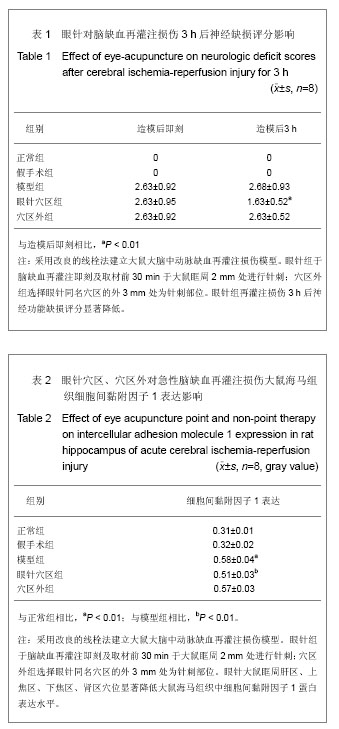
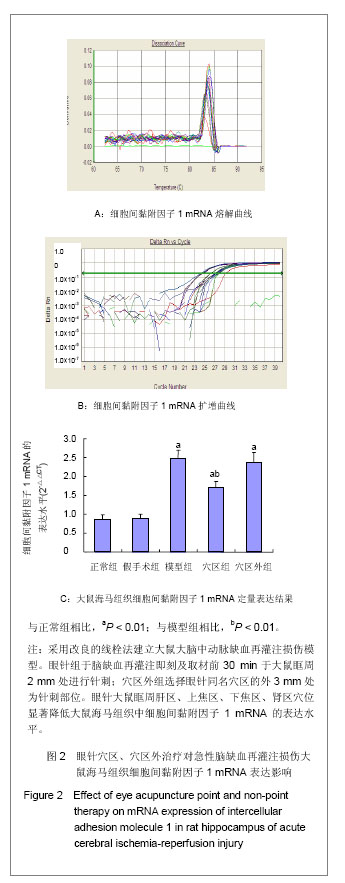
背景:病理情况下,细胞间黏附因子1表达明显升高,促进炎症反应的发生,加重脑组织损伤。 目的:观察眼针穴区、穴区外治疗对急性脑缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠海马组织细胞间黏附因子1表达的影响。 方法:40只SD大鼠随机等分为正常组、假手术组、模型组、眼针穴区组和穴区外组。后3组用线栓法复制脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠模型,栓塞线插入深度1.8-2.2 cm,眼针组于脑缺血再灌注即刻及取材前30 min,取肝区、上焦区、下焦区、肾区平刺眼眶周治疗20 min。穴区外组选择眼针同名穴区的外3 mm处为针刺部位,刺法与眼针穴区相同。 结果与结论:眼针穴区治疗后大鼠神经功能缺损评分下降,海马组织细胞间黏附因子1蛋白及mRNA表达显著降低(P < 0.01)。穴区外组治疗后大鼠神经功能缺损评分及海马组织细胞间黏附因子1蛋白及mRNA表达无明显变化。提示眼针具有明显的改善大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的作用,其机制与下调海马组织细胞间黏附因子表达有关。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)